Low AMH
Treatments
- Endometrial Receptivity Array
- PGD
- PGS
- Blastocyst Transfer
- ICSI
- Endometrial Scratching
- Autoimmune Diseases
- Weight Loss Management
Endometrial Receptivity Array
What is it?
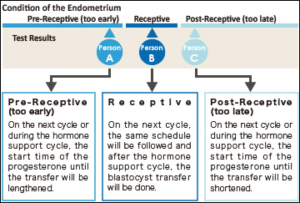 The term ERA stands for Endometrial Receptivity Analysis or Array. In this test, a small sample tissue from endometrial lining (innermost layer of Uterus) is used for evaluating whether the Uterus is ready for implantation of embryo or not.
The term ERA stands for Endometrial Receptivity Analysis or Array. In this test, a small sample tissue from endometrial lining (innermost layer of Uterus) is used for evaluating whether the Uterus is ready for implantation of embryo or not.
In the menstrual cycle of a woman the period from 19th to 23rd days is known as “implantation window” during which, the uterus gets prepared for the implantation process. It is part of the luteal phase and the endocrine part of ovaries is producing progesterone. This progesterone brings about modifications in the uterine wall so that, it gets prepared for receiving the embryo. The process involves formation of certain proteins that make the lining thicker and more receptive. In majority of females (84%) this window occurs at the exact time while in very few females (16%) this window occurs either before or after this period.
The IVF treatment in such cases fails as, the embryo transfer is occurring at wrong time. It is happening at the time, when the implantation window is either yet to open or has already been closed. So, the implantation is failing.
When is it prescribed?
It is prescribed in the patients where recurrent implantation failures are observed.
How is it done?
- A small endometrial tissue is collected and expression level of the gene 238 which determines endometrial receptivity is investigated.
- The technique involves assessing RNA levels in different stages of menstrual cycle. As this test is reproducible, its findings remain the same months after and hence, the test is not required to be repeated.
- This investigation can clearly indicate whether this implantation window of a particular woman is happening at the right time or the embryo transfer needs to be scheduled on the different date to match the window so that maturation of endometrial lining can be synchronized with embryo.
What are the advantages?
- Due to precise identification of Implantation Window, embryo transfer can be appropriately planned and can yield assured results.
- The agony of failed transfer can be got rid of.
- A minor shift by one of two days in embryo transfer can result into pregnancy.
PGD - Pre-implantation Genetic Diagnosis
What is it?
Pre-implantation Genetic Diagnosis is genetic screening technique which allows an expert to examine the genetic composition of a pre-embryo before it is transferred to the patient’s uterus so that, transmission of hereditary disorders into next generation can be avoided.
Why is it recommended?
A normal human genetic code consists of 23 pairs of chromosomes, and each of the chromosomes may contain hundreds of genes. This genetic material is inherited from gametic cells of both mother and father. The combination of these genes creates the character blueprint for the offspring. Unfortunately, the process may not always work seamlessly. Disorders in the chromosomes or particular gene lead to complications in pregnancy or miscarriage or serious genetic diseases. PGD can help in identification of the issues well before the pregnancy occurs.
In an IVF cycle, the embryos are selected using visual criteria: the embryo or embryos that look healthy are chosen for transfer. Sometimes, a visual inspection is not enough. Some serious genetic abnormalities are invisible to the eye. This is where PGD can be used. Following hereditary abnormalities can be identified with PGD:
- Turner’s syndrome.
- Klinefelter’s syndrome.
- Translocation which can cause miscarriages or some forms of leukemia or cancer.
- Cystic fibrosis.
- Tay-Sachs disease.
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
- Sickle-cell anemia.
When is it recommended?
PGD can be recommended in following conditions:
- Women age 35 and older because there is a concern about the genetic quality of their eggs.
- Women experiencing recurrent, unexplained pregnancy loss.
- Women with more than one failed fertility treatment.
- Carriers of sex-linked disorders – they can choose gender determination to prevent sex-linked disease.
- Carriers of single gene disorders.
- Couples with family history of inherited disease.
- Those with chromosomal disorders.
What are the advantages?
- Avoids the need for amniocentesis (with a needle and syringe, some amniotic fluid from around the embryo is drawn for pre-natal examination) which be an uncomfortable technique and involves some risk.
- Enables the selection and implantation of healthy pre-embryo resulting into better chances of pregnancy and lower possibility of miscarriage.
- With proper screening fewer embryos are used for transfer thus, minimizing possibility of multiple births.
PGS - Pre-implantation Genetic Screening
What is it?
It is the genetic study of embryo produced during IVF treatment & can help in having a healthy baby. The technique is helpful to identify embryos with the correct number of chromosomes for successful fertility treatment. PGS is performed on the embryo before it is transferred. This allows the identification & transfer of embryos free from any hereditary abnormalities.
When is it recommended?
It is recommended under following conditions:
- If the female partner is more than 35 years.
- The female has suffered 2 or more miscarriages.
- There is history of previous IVF failures.
- Infertility is due to some male factor.
What are the advantages?
- Reduced miscarriage rates.
- Higher pregnancy rate per transfer.
- Greater chances of having a healthy baby.
Blastocyst Transfer
What is it?
The embryo formation after fertilization involves a number of stages such as 2 cell, 4 cells, 8 cells stage, Morula and so on. Gradually, the cells become distinct as outer cells (Trophoblast) and inner cell mass (embryonic cells). There is a small cavity in between. This stage is called blastocyst. Usually, the protective covering of embryo (Zona Pellucida) is still intact. The blastocyst hatches out of this covering to get implanted into endometrial lining (Innermost covering of uterus).
Using this blastocyst (developed in laboratory) for embryo transfer in IVF technique is called blastocyst transfer (Blast transfer).
When is it recommended?
Blast transfer is recommended for those patients with one more of the following conditions.
- The patients of higher age (35 years or more).
- Repeatedly failed IVF cycles.
- Recipient patients (who are receiving eggs or embryos from donor).
- Those who don’t have the mental preparation for further IVF cycles.
What are the advantages?
- Higher success rates even for patients of higher age.
- Growth pattern of the embryo is established in the laboratory before implantation. So, the doctor has a clear understanding about progress of embryo after implantation.
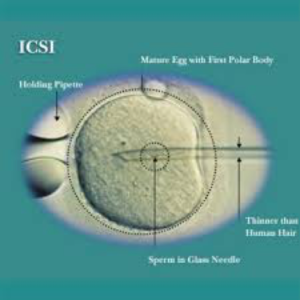
ICSI
What is it?
It is a laboratory procedure where a single sperm is picked up with a fine glass needle and is injected directly into the egg. This is carried out in the laboratory by experienced embryologists using special equipment.
When is it recommended?
It is recommended in any or more of the following conditions.
- When the sperm count is very low
- When the sperm cannot move properly or are in other ways abnormal
- When sperm has been retrieved surgically from the epididymis (MESA/PESA) or the testes
- (TESE/TESA), from urine or following electro-ejaculation
- When there are high levels of antibodies in the semen
- When there has been a previous fertilisation failure using conventional IVF.
What are the advantages?
 Very few sperms are required for the process and the ability of the sperm to penetrate the egg is no longer important as this has been assisted by the ICSI technique. ICSI does not guarantee that fertilisation will occur as the normal cellular events like fusion of nuclei still need to occur once the sperm has been placed in the egg.
Very few sperms are required for the process and the ability of the sperm to penetrate the egg is no longer important as this has been assisted by the ICSI technique. ICSI does not guarantee that fertilisation will occur as the normal cellular events like fusion of nuclei still need to occur once the sperm has been placed in the egg.
Endometrial Scratching
What is it?
An endometrial scratch is a procedure proposed to improve endometrial (innermost lining of Uterus) receptivity and increase the probability of pregnancy in women undergoing IVF.
When is it recommended?
- Patients that have experienced recurrent unsuccessful IVF cycles, with good quality embryos, the fertility specialist may suggest performing an endometrial biopsy or hysteroscopy to investigate for potential endometrial causes of implantation failure, such as intrauterine adhesion, endometrial polyps etc.
- It is generally only used for patients who have experienced multiple unsuccessful IVF cycles, despite the transfer of good quality embryos.
Autoimmune Diseases
What is it?
This is a condition in which the defense mechanism of the body starts identifying normal body cells are foreign cells and starts destroying them. In short, the immune system has been misguided against own body cells and can lead to serious consequences. This kind of disorder can affect endocrines, muscles, digestive system or gonadal organs (Testis or Ovary). Effects on endocrines or gonadal organs can result into infertility. Immunity against ovary minimized the ovarian reserve.
How is it diagnosed?
Autoimmune disease affecting ovary can be diagnosed by checking the ovarian reserve. This is done by analyzing the levels of FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) and AMH (Anti Mullerian Hormone) in blood. Abnormally excess values of these hormone for a particular age could be due to reduced ovarian reserve and is likely to cause early menopause or infertility.
What are various autoimmune diseases?
Thyroid disease: Thyroid gland plays very important role in most of the body activities. Its autoimmunity in women, can reduce the pregnancy rate and can lead to miscarriage.
Anti-sperm Antibodies: Some times in men, antibodies are generated against own sperms. This may reduce the number or motility of sperm and reduce the chances of fertilization in female partner. The men who have had history of testicular trauma or surgery, reversal of vasectomy or treatment for varicocele are likely to have this type of antibodies.
Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome: This is a disorder in which antibodies are generated against a particular component of placental tissue resulting into miscarriage, certain pregnancy complication or placental abruption.
How is it treated?
Once diagnosed, the particular disease can be treated with appropriate medication and possibility of conception can be increased. Specific fertility treatment can provide a respite.
Weight Loss Management
What is it?
It is avoiding weight gain or losing weight for improving the chances of conceiving. Too low or too high body weight can interfere with fertility of an individual and hence, needs to be managed appropriately.
How is it done?
Normally, weight loss management involved diet and exercise. The couple trying for pregnancy needs to take careful measures in this. Proper diet and moderate exercise are best recommended for weight loss. But during pregnancy if necessary, weight management must be done preferably by diet control. Heavy exercise can affect the embryonic development in uterus and hence, has to be avoided.
When is it recommended?
Excess body weight in female partner is known to reduce the possibility or pregnancy. There is a need to manage the weight appropriately for natural pregnancy or even IVF. When an obese patient approaches for IVF treatment, before treatment the patient needs to undergo weight management regime and only then the IVF protocol can be followed. As mentioned above, the weight loss should be by controlled diet and not entirely by exercise.
